One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process P=P0/(2+V0/V),(where P0 and V0 are constant).Change in temperature of the gas when volume is changed from V=V0 to V =3V0 is

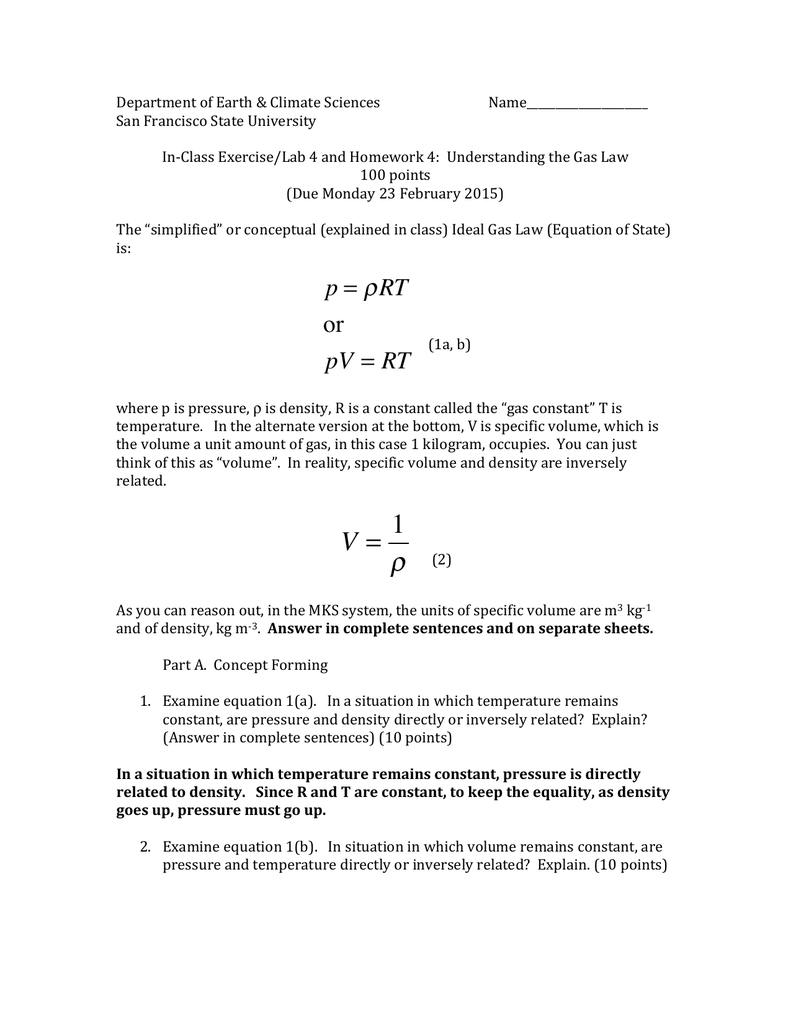
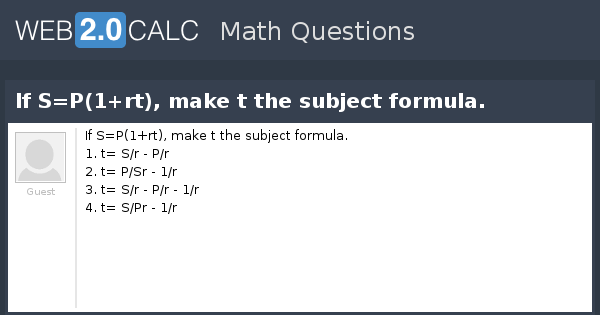
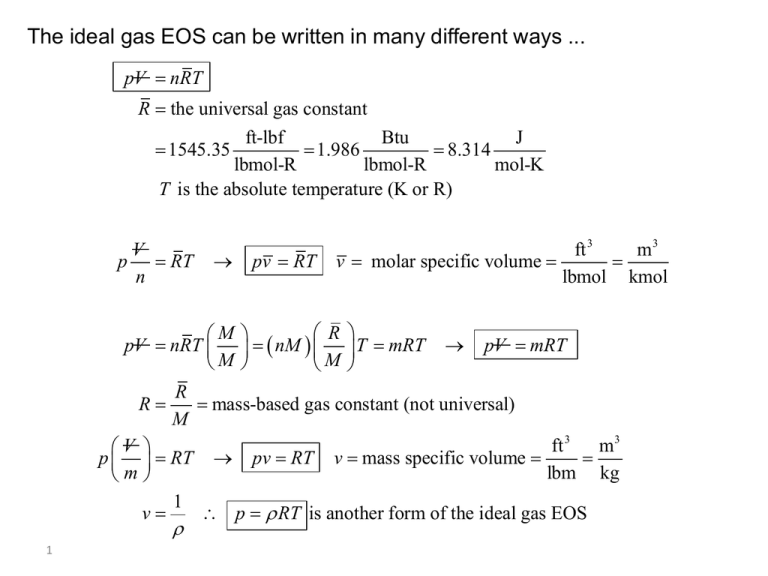
Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT re-arrange n V = P RT n = molar mass (g/mol) mol gas= mass gas (g) mass of sample V x molar mass = P RT =

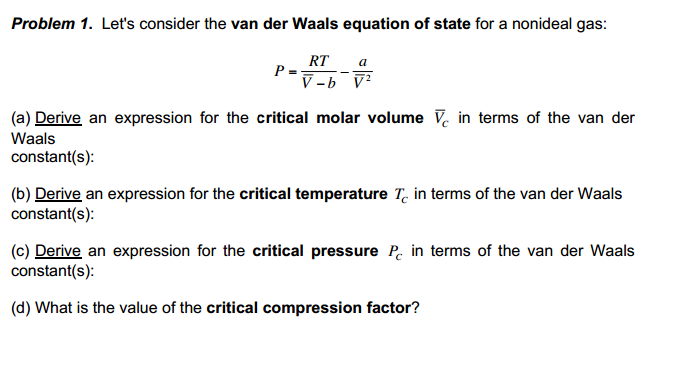
The van der waals equation for a gas is (P + a/v2)(V-b) = RT where P = Pressure, V = - Physics - Units And Measurements - 2236057 | Meritnation.com

Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT re-arrange n V = P RT n = molar mass (g/mol) mol gas= mass gas (g) mass of sample V x molar mass = P RT =
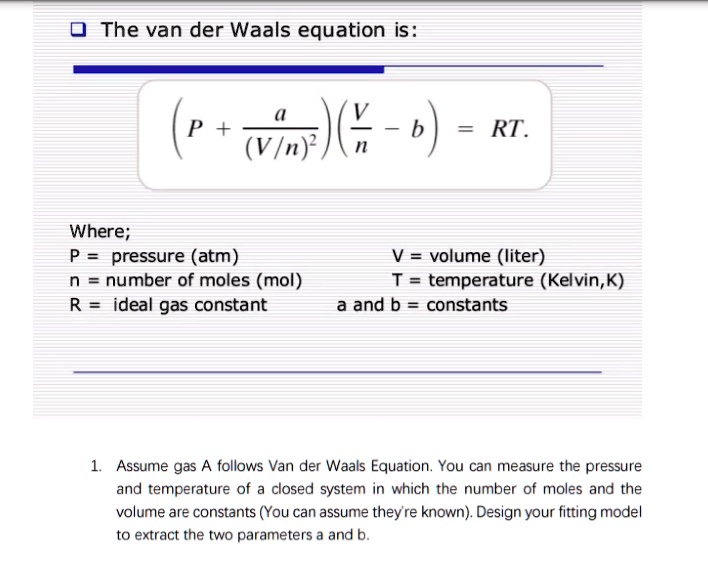
SOLVED: The van der Waals equation is: P + Wo) = b RT. Where; P = pressure (atm) n = number of moles (mol) R = ideal gas constant V = volume (

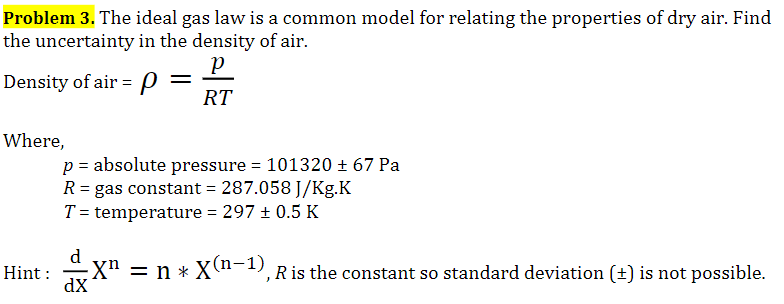
Ideal-Gas Equation The constant of proportionality is known as R, the gas constant. © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. - ppt download